

Fiber-optic communications is based on the principle that light in a glass medium can carry more information over longer distances than electrical signals can carry in a copper or coaxial medium or radio frequencies through a wireless medium. The purity of today’s glass fiber, combined with improved system electronics, enables fiber to transmit digitized light signals hundreds of kilometers without amplification. With few transmission losses, low interference, and high bandwidth potential, optical fiber is an almost ideal transmission medium. To use the light to transmit the signals from one place to another place over optic fiber, is due to the light propagates through the fiber with little attenuation also immune to electromagnetic interference. These advantages also contribute to fiber optic development and practical application. Lenora solution includes a full range of optic devices, fiber optic cables, and also the accessories like pigtails, patch cords, adapters and different type’s terminal boxes. Lenora has complete ranges of these components with low attenuation loss control, combines with fiber optic cables, support the complete channel with good headroom margin. Lenora has the capability and capacity to support a large global network of Telecommunication from and to any point in the supply chain, Our Advanced equipment enable the production and supply of exceptionally high quality and performance devices played a key role in integration technology of fiber cable products and solution all over the world. And make it easier for our customers to innovate, compete and continue to drive down the cost of optical Telecommunication hardware worldwide.

How are Fiber Optics used today? Today, practically every communication network contains fiber optics. In most cases, fiber optics are used because of their convenience. Fiber optic cable allows network builders to divide their network into smaller service areas that prevent large numbers of customers from being affected in an outage. The result is better service and customer relations. Fiber optic cable also gives them a fast return path which they use for internet and telephone connections, thereby increasing their revenue potential. Local Area Networks (LANs) use fiber optics primarily in the backbone of the network, but the use of fiber optics to the desk is increasing. The LAN backbone often needs longer distance transmissions and more bandwidth than copper cable is capable of providing. Fiber easily offers the higher bandwidth needed to prepare the network for the much higher speeds projected for the near future. The use of fiber optics is not just limited to communication networks. Cable and telephone providers often use fiber for its distance capabilities. Distance is also an advantage to industrial plants that use vast amounts of fiber primarily for its noise immunity. Utilities also prefer fiber for noise immunity, security and high bandwidth properties. The military uses fiber because it’s nearly tap-proof and impossible to jam. Fiber is even used by the aviation and aerospace industries because of its smaller size and weight.
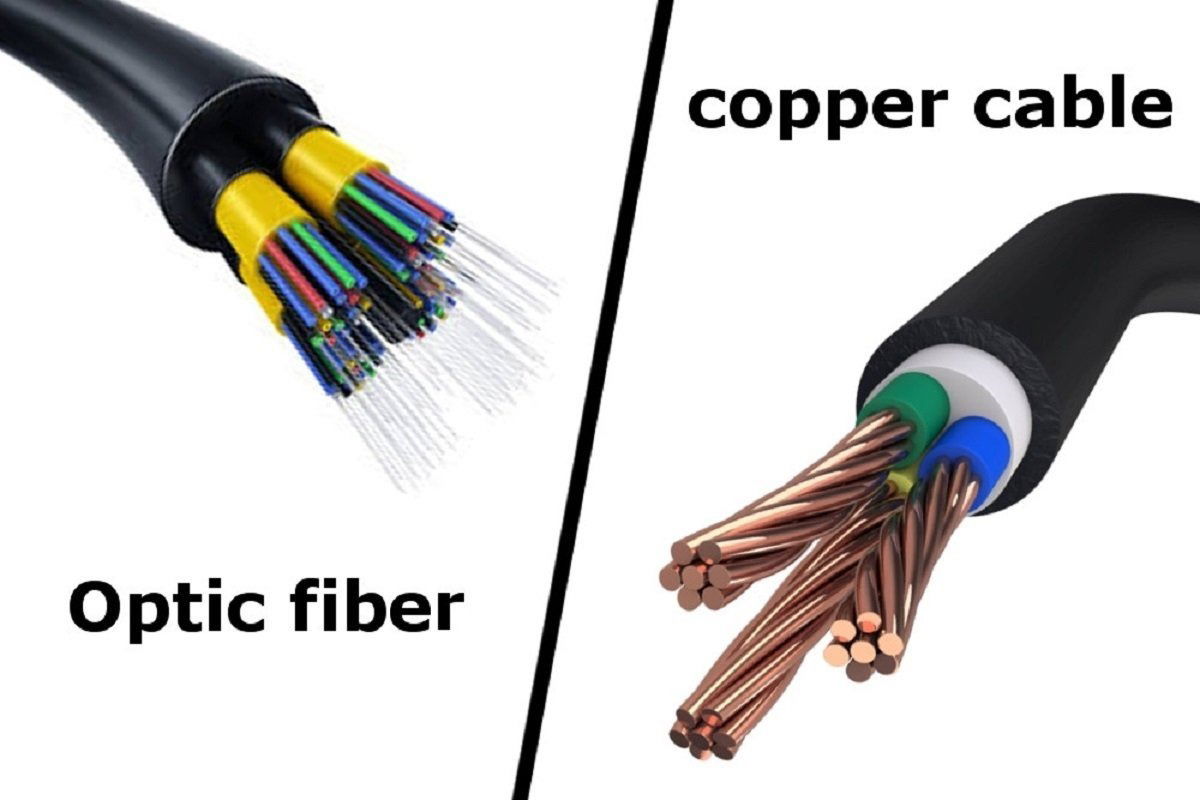
What are the advantages of Fiber Optics over Copper wire? Fiber’s extra distance capability and seemingly unlimited data rate makes it possible to do things not possible with copper wire. For example, you can install all the electronics for a network in one communications closet for a building and run straight to the desk with fiber. With copper, you can only transmit about 90 meters, thus requiring more telecom closets in each building. With fiber, you only need passive patch panels locally to allow for moves. Upgrades can be rather difficult with copper wire, but not with fiber because the real capacity of fiber is only partially utilized at today’s network speed. Many uses fiber to connect all their central offices and long distance switches because it has thousands of times the bandwidth of copper wire and can carry signals hundreds of times further before needing a repeater. The cable and telephone providers use fiber because it gives them greater reliability with the opportunity to offer new services, like digital phone service and internet connections. They also use fiber for economic reasons, but their cost justification requires adopting new network architectures to take advantage of the fiber’s strengths.